Nephrologische Forschung

Translationale und experimentelle Nephrologie
Arbeitsgruppe von Vietinghoff
Members
Lab manager and technician
Julia Miranda, BA
Postdoctoral researchers
Dr. Peyman Falahat
Dr. Uta Scheidt
Dr. Georg Sendtner
Dr. Hagen Ehleiter
Graduate students
Adrian Goldspink, MA, PhD student
Lena Possenriede, MA, PhD student
Maria Deligiorgi, MA, Phd student
Leonie Richard, MD student
Pia Naumann, MD student
Maximilian Weiss, MD student
Pelin Guels, MD student
Research interest
We investigate the role and regulation of leukocytes in vascular inflammation in renal failure.
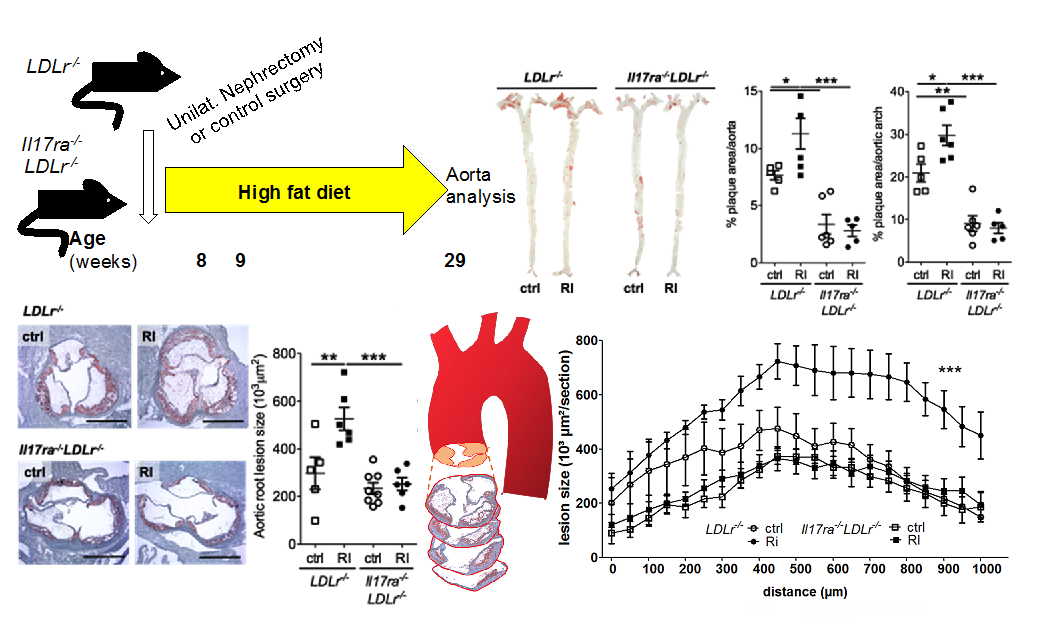
Chronic kidney disease affects a large proportion of the population. It impairs host response to pathogens but also increases atherosclerotic inflammation and mortality. Chronic inflammation of the arterial wall is a major contributor to atherosclerotic plaque growth and instability.
We investigate innate immune cells and the vascular inflammatory infiltrate in patients with chronic kidney disease and mouse models of atherosclerosis. A focus of our work has been the role of the T cell cytokine Interleukin 17 in regulation of innate immune cells (Ge et al., 2013, Dong et al, 2016, Nordlohne et al., 2018, Roy-Chowdhury et al., 2021, Huesing et al., 2022). Current projects include translational approaches assessing vascular function and immune parameters in patients with kidney disease (Dr. Scheidt).
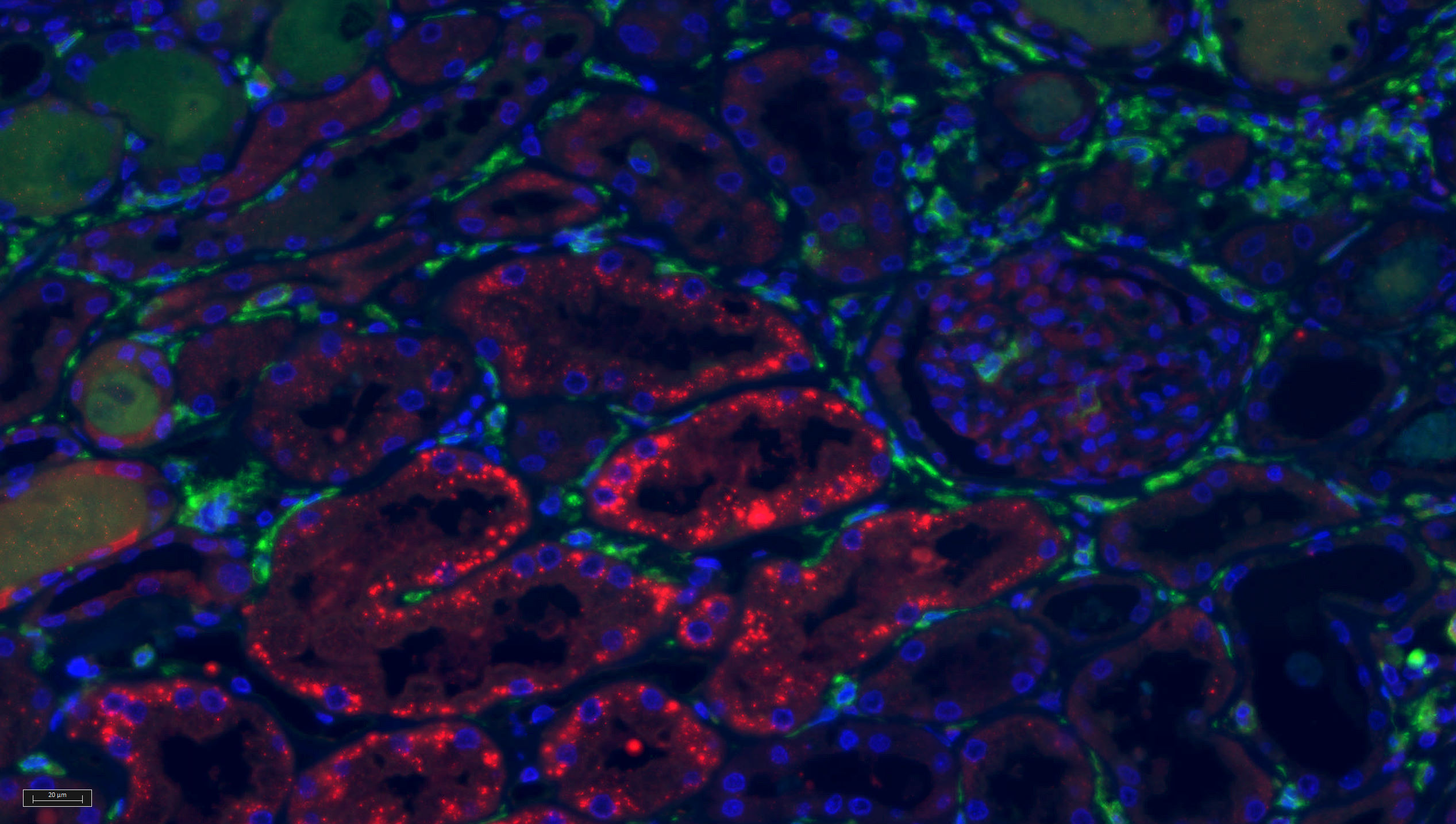
Kidney innate leukocytes, especially neutrophilic granulocytes and monocytes and macrophages are central for chronic renal inflammation and host response. Our projects have investigated kidney macrophages after transplantation and correlated their abundance with transplant survival and complications such as urinary tract infections. A recent study elucidated how renal electrolytes urea and NaCl impact on chemokine production of renal tubular epithelium (Schmitz, Brauns et al., European Journal of Immunology 2022).
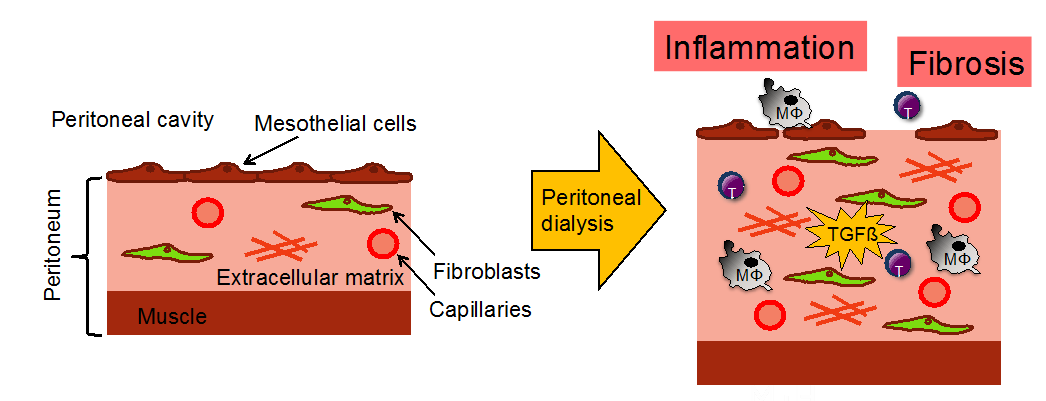
Peritoneal dialysis is an important mode of renal replacement therapy. It can be a successful for years or fail due to peritoneal membrane thickening and inflammatory changes. We use our immunologic interest to better understand macrophage crosstalk with the peritoneal membrane.
In summary, we aim to improve mechanistic understanding of innate inflammation in renal impairment with the goal to define specific treatment avenues.
Our work is currently supported by
Excellence Cluster Immunosensation, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and others
Selected publications:
1.Goldspink A*, Schmitz J*, Babyak O, Brauns N, Milleck J, Breloh AM, Fleig SV, Jobin K, Schwarz L, Haller H, Wagenlehner F, Bräsen JH, Kurts C, von Vietinghoff S. Kidney medullary sodium chloride concentrations induce neutrophil and monocyte extracellular DNA traps that defend against pyelonephritis in vivo. Kidney Int. 2023 Aug;104(2):279-292.. *shared first authorship
2. Hüsing A, Wulfmeyer V, Gaedcke S, Fleig S, Rong S, DeLuca D, Haller H, Schmitt R, von Vietinghoff S.
Myeloid CCR2 Promotes Atherosclerosis after Acute Kidney Injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 May 10:ASN.2022010048. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2022010048.
3. Helmke A, Hüsing AM, Gaedcke S, Brauns N, Balzer MS, Reinhardt M, Hiss M, Shushakova N, de Luca D, Prinz I, Haller H, von Vietinghoff S.
Peritoneal dialysate-range hypertonic glucose promotes T cell IL-17 production that induces mesothelial inflammation.
Eur J Immunol. 2020 Sep 14. doi: 10.1002/eji.202048733.
4. Roy-Chowdhury E, Brauns N, Helmke A, Nordlohne J, Bräsen JH, Schmitz J, Volkmann J, Fleig SV, Kusche-Vihrog K, Haller H, von Vietinghoff S.
Human CD16+ monocytes promote a pro-atherosclerotic endothelial cell phenotype via CX3CR1-CX3CL1 interaction.
Cardiovascular Research 2020, Jul 27:cvaa234. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa234.
5. Helmke A*, Nordlohne J*, Balzer MS, Dong L, Rong S, Hiss M, Shushakova N, Haller H, von Vietinghoff, S.
CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction mediates macrophage-mesothelial crosstalk that promotes peritoneal fibrosis in vivo.
Kidney international in press 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.12.030.
6. Helmke A, Casper J, Nordlohne J, David S, Haller H, Zeisberg E, von Vietinghoff S.
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition shapes the atherosclerotic plaque and modulates macrophage function.
FASEB J. 2019 Feb;33(2):2278-2289.
7. Casper J*, Schmitz J*, Bräsen JH, Khalifa A, Schmidt BMW, Einecke G, Haller H, von Vietinghoff S.
Renal transplant recipients receiving loop diuretic therapy have increased urinary tract infection rate and altered medullary macrophage polarization marker expression.
Kidney International 2018 Nov;94(5):993-1001.
8. Nordlohne J, Helmke A, Ge S, Rong S, Chen R, Waisman A, Haller H, von Vietinghoff, S.
Aggravated atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation with reduced kidney function depend on Interleukin-17 eceptor A and are normalized by inhibition of IL-17A.
JACC Basic to translational Science Jan 2018 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacbts.2017.08.005
9. Bräsen JH, Khalifa A, Schmitz J, Dai W, Einecke G, Schwarz A, Hallensleben M, Schmidt BMW, Kreipe HH, Haller H, von Vietinghoff S.
Macrophage density in early surveillance biopsies predicts future renal transplant function.
Kidney international 2017 Aug;92(2):479-489.
10. Dong L*, Nordlohne J*, Ge S, Hertel B, Melk A, Rong S, Haller H, von Vietinghoff S.
T Cell CX3CR1 Mediates Excess Atherosclerotic Inflammation in Renal Impairment.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jun;27(6):1753-64.
11. Ge S, Hertel B, Koltsova EK, Sörensen-Zender I, Kielstein JT, Ley K, Haller H, von Vietinghoff S.
Increased atherosclerotic lesion formation and vascular leukocyte accumulation in renal impairment are mediated by Interleukin 17A.
Circ Res. 2013 Sep 27;113(8):965-74.
AG Klinische Prädiktion (OA Dr. Schwab)
Mitglieder:

Dr. Sebastian Schwab, Nephrologe, Oberarzt
Michel Brodesser (Med. Doktorand)
Biomarker zur Vorhersage von Nierenfunktion und kardiovaskulären Komplikationen
Die Einschätzung der Nierenfunktion erfolgt überwiegend über die Bestimmung von Serum-Kreatinin und Serum-Cystatin C als Grundlage für die Berechnung der glomerulären Filtrationsrate (eGFR), aber auch für die Einteilung des Schweregrades, und für die Abschätzung der Prognose der Nierenkrankheit. Kreatinin, Cystatin C und die Albuminurie, die am häufigsten verwendeten Messwerte zur Beurteilung der Nierenfunktion respektive des funktionellen Nierenschadens, spiegeln in erster Linie die Integrität der Glomeruli wider und erfassen als „glomerulozentrische“ Betrachtung keine Tubulusfunktionen wie die Reabsorption gefilterter Moleküle, die Abwehr von Infektionen, die Proteinsynthese sowie Sekretion und die Regulation der Säure-Basen-Homöostase. Auch bei der akuten Nierenfunktionsverschlechterung sind die Eckpfeiler der Diagnostik Veränderungen des Serumkreatinins sowie der Urinausscheidung und damit unspezifisch.
Die Einschätzung der residualen Nierenfunktion bei Dialysepatienten ist im Vergleich zu chronischen, nicht-dialysepflichtigen Patienten sehr viel schwieriger. Die Restnierenfunktion hat besonders bei Hämodialysepatienten eine große Bedeutung, vor allem in Bezug auf kardiovaskuläre Morbidität und Mortalität, zumal kardiovaskuläre Erkrankungen weiterhin die häufigste Todesursache bei Nierentransplantationsempfängern sind.
Zusammenfassend befasst sich die Arbeitsgruppe mit der diagnostischen Wertigkeit von verschiedenen glomerulären und tubulären Biomarkern sowie der Prädiktion eines fortschreitenden Nierenfunktionsverlustes und kardiovaskuläre Ereignisse.
Ausgewählte Publikationen:
Peritoneal and renal DKK3 clearance in peritoneal dialysis.
Ehleiter H, Miranda J, Boes D, Scheidt U, von Vietinghoff S, Schwab S. BMC Nephrol. 2024 Aug 23,25(1):268
Recent Insights in Noninvasive Diagnostic for the Assessment of Kidney and Cardiovascular Outcome in Kidney Transplant Recipients.
Falahat P, Scheidt U, Pörner D, Schwab S. J Clin Med. 2024 Jun 27;13(13):3778. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133778. PMID: 38999343 Free PMC article. Review.
NT-proBNP as predictor of major cardiac events after renal transplantation in patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction.
Schwab S, Pörner D, Kleine CE, Werberich R, Werberich L, Reinhard S, Bös D, Strassburg CP, von Vietinghoff S, Lutz P, Woitas RP. BMC Nephrol. 2023 Feb 11;24(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03082-9.
Pre-transplant serum Beta Trace Protein indicates risk for post-transplant major cardiac adverse events.
Schwab S, Pörner D, Kleine CE, Werberich R, Werberich L, Reinhard S, Bös D, Strassburg CP, von Vietinghoff S, Lutz P, Woitas RP. Nephrology (Carlton). 2023 Jan;28(1):51-59. doi: 10.1111/nep.14131. Epub 2022 Nov 21.
Beta-trace protein as a potential biomarker of residual renal function in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis.
Schwab S, Kleine CE, Bös D, Bohmann S, Strassburg CP, Lutz P, Woitas RP. BMC Nephrol. 2021 Mar 11;22(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02287-0. PMID: 33706697